

For example, a 100% dose of noise (the maximum amount allowed) is equivalent to 8 hours of exposure at 90 dBA, 4 hours at 95 dBA, 2 hours at 100 dBA … all the way to ¼ hour at 115 dBA. An allowance of louder noise exposures for shorter periods of time for compliance with the PEL, as long as the TWA exposure does not exceed 90 dBA.A TWA exposure is the average noise exposure as integrated over an 8-hour monitoring duration.
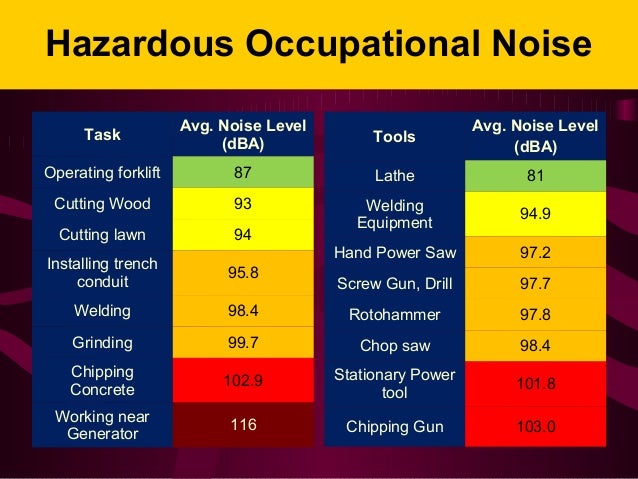
A permissible exposure limit (PEL) of 90 decibels, A-scale (dBA) as an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA).Key provisions of OSHA’s noise standard include: That’s why the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) published a permissible exposure limit (PEL) in 1971, and later published the Hearing Conservation Amendment in 1980 which included an Action Level that (if exceeded) required a Hearing Conservation Program designed to proactively manage exposures to elevated noise levels in the workplace. We’ll start to notice that we can’t hear light rain falling on the roof, birds singing in early spring, leaves rustling on an autumn day, and many other sounds that are important to a great quality of life. With elevated and repeated occupational noise exposure over a long period of time, we simply can’t hear nearly as well as we did early in life. Our hearing typically recovers in a few days from these types of exposures.īut did you know that elevated and repeated occupational noise exposures (well below these short-term and occasional exposures) can, over many years, cause gradual but significant hearing loss? Noise exposure measurement records should be kept for 2 years and audiometric test results must be kept for the duration of the employee’s employment.Many of us have experienced temporary hearing loss (known as a temporary threshold shift) from very loud impact noises such as from firecrackers or shooting firearms, and from occasional loud exposures during concerts or sporting events.If an STS is present, the employer must obtain a retest within 30 days and consider the results of the retest as the annual audiogram.Employee’s annual audiograms should be compared to their baseline audiogram to determine the validity and if an STS has occurred.Audiometric tests will be performed by a licensed physician, audiologist, or certified technician.
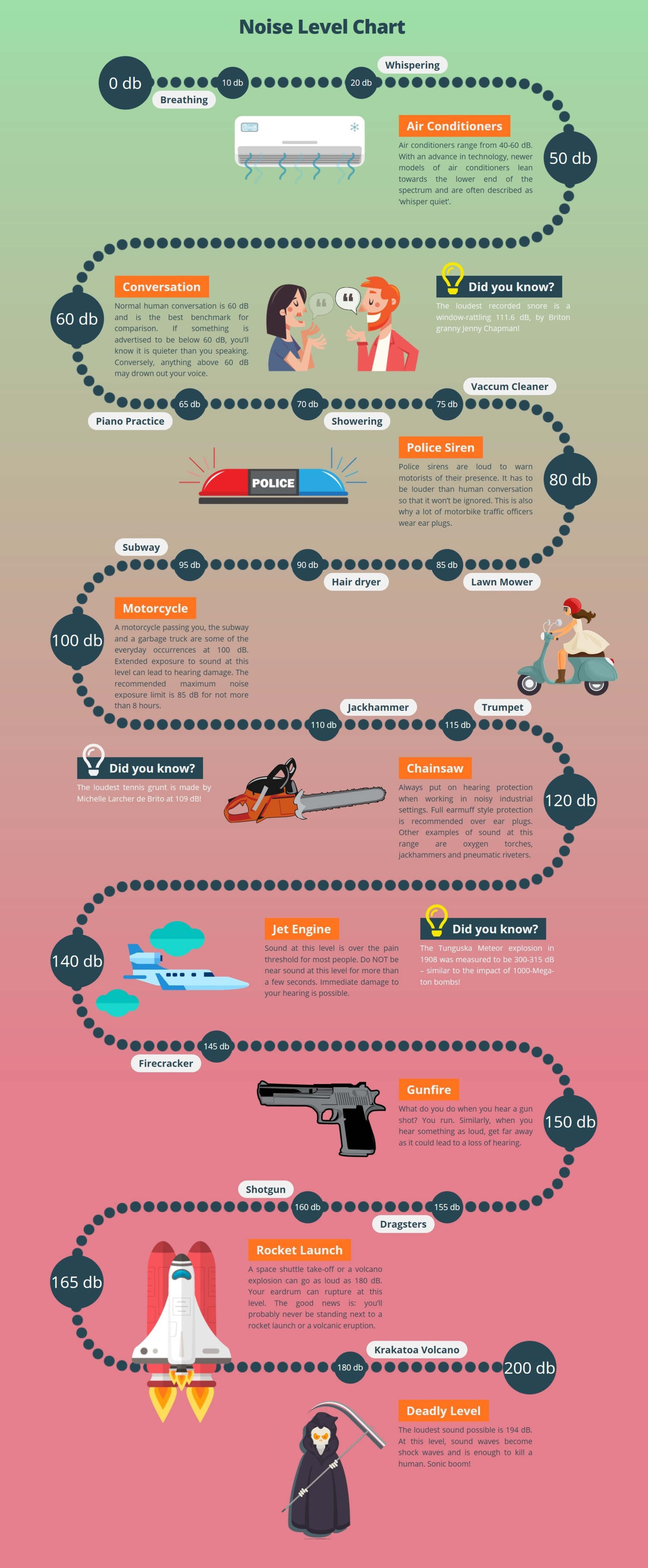
The program should be available at no cost to employees.Establish and maintain an audiometric testing program available to all employees whose exposures equal or exceed 85 dB over an 8-hour time-weighted average.Employers should maintain a Hearing Conservation program to include monitoring, testing, follow-up, training, and recordkeeping.OSHA requires employers to provide a safe workplace for all of their employees. What are OSHA’s Audiometric Testing Regulations? If an employee is urged to seek a physician, the employer must pay for any referrals that are intended to identify the effects of occupational noise exposure or from wearing the required hearing protection. A medical referral is required if an employee is unable to take a test, does not respond reliably, or has irritation or pain in the ear canal caused by protection such as earplugs.
Osha decibel chart professional#
Some employees may need to seek a physician if the testing professional believes that the test may have been inaccurate or that there is a larger problem at play. The fitted hearing protectors should be comfortable and offer sufficient protection to prevent hearing loss. Employees should wear hearing protectors if they are exposed to 8-hour Time-Weighted Average (TWA) noise levels of 85 dB or more. An STS or standard threshold shift refers to a shift in either ear of 10dB or more at 2,000-4,000 hertz. After the audiograms have been completed, the employer must fit any employees showing an STS with adequate hearing protectors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
